
We seek to determine the length of a curve that represents The graph of created Concentrate on the segment whose length is Li. Those of you who are interested in the details should consult an advanced calculus text. Calculus II MAT 146 Integration Applications: Arc Length Again we use a definite integral to sum an infinite number of measures, each infinitesimally small. Here, we require f(x) to be differentiable, and furthermore we require its derivative, approach x. However, for calculating arc length we have a more stringent requirement for f(x). As shown here, this is not a Riemann Sum. Summing over all subintervals gives an arc length approximation L n i 1dx2 i + y2 i. )' part of the Arc Length Formula guarantees we get at least the distance between x values, such as this case where f’ (x) is zero. In previous applications of integration, we required the function f(x) to be integrable, or at most continuous. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the length of this line segment is dx2 i + y2 i. Well of course it is, but it's nice that we came up with the right answer Interesting point: the ' (1 +. (The process is identical, with the roles of x and y reversed.) The techniques we use to find arc length can be extended to find the surface area of a surface of revolution, and we close the section with an examination of this concept.Īrc Length of the Curve y = f(x) We begin by calculating the arc length of curves defined as functions of x, then we examine the same process for curves defined as functions of y. Now, suppose that this curve can also be defined by parametric. Or, if a curve on a map represents a road, we might want to know how far we have to drive to reach our destination. The arc length L of such a curve is given by the definite integral. If a rocket is launched along a parabolic path, we might want to know how far the rocket travels.

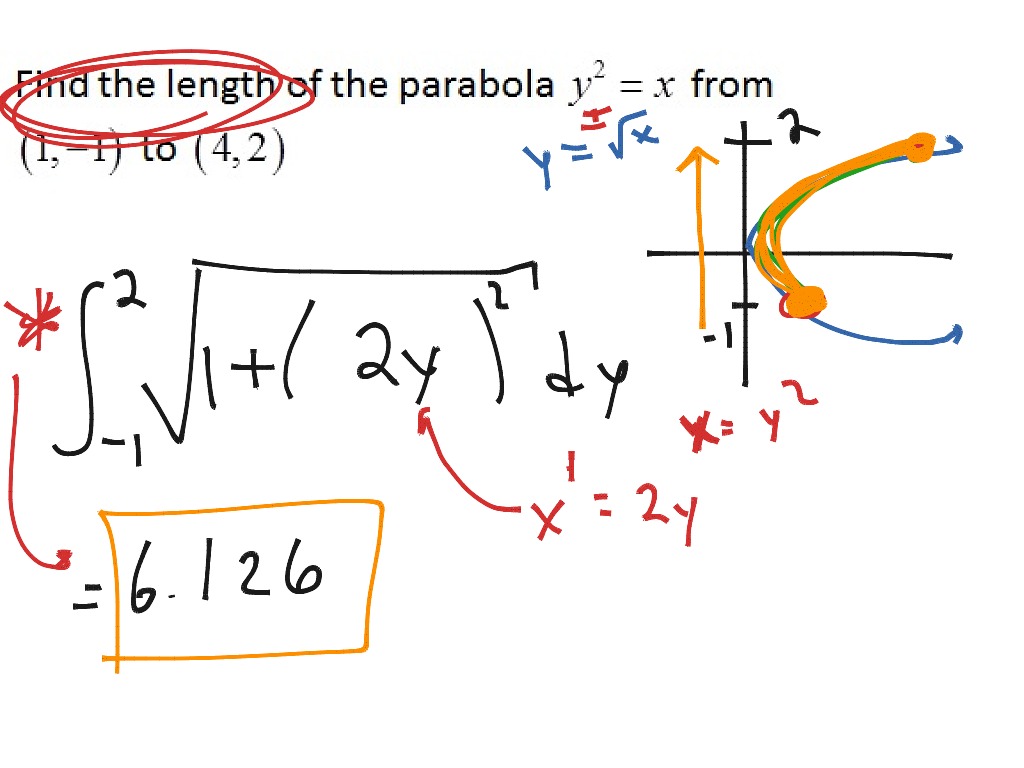
Many real-world applications involve arc length. We can think of arc length as the distance you would travel if you were walking along the path of the curve. In this section, we use definite integrals to find the arc length of a curve. Similarly, if xg(y) with g continuously differentiable on c,d, then the arc length L of g(y) over c,d is given by Ldc1+g(y)2dy. Find the surface area of a solid of revolution.Determine the length of a curve, x=g(y), between two points.

Suppose that a curve C is described by the parametric equations x=f(t), y=g(t), $$$ $$$. We are going to define the length of a general curve by first approximating it by a polygon and then taking a limit as the number of segments of the polygon is increased. We use the same approach as with areas and volumes. We know that for the angle equal to 360 degrees (2), the arc length is equal to circumference. However, in general it can be very diffcult to find length of some curve. Arc length formula The length of an arc depends on the radius of a circle and the central angle. (We can use the distance formula to find the distance between the endpoints of each segment.)

If the curve is a polygon, we can easily find its length we just add the lengths of the line segments that form the polygon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
